Did you know that something as simple as slouching when sitting can potentially lead to a painful condition called pilonidal cyst? While it may seem harmless, the act of slouching can put pressure on the coccyx (tailbone) and the surrounding area, increasing the risk of pilonidal cyst formation. In this article, we will explore how slouching can contribute to the development of this condition and the importance of maintaining proper posture to prevent it. So, if you're someone who tends to slouch while sitting, it's time to straighten up and pay attention!
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Risk factor | Yes |
| Prolonged sitting | Yes |
| Poor posture | Yes |
| Pressure on the coccyx area | Yes |
| Restricted blood flow | Yes |
| Friction and irritation | Yes |
| Sweat and moisture | Yes |
| Hair growth | Yes |
| Poor hygiene | Yes |
| Genetics | Yes |
What You'll Learn
- Is there a connection between slouching when sitting and the development of pilonidal cysts?
- Can poor posture contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts?
- How does slouching lead to the development of pilonidal cysts?
- Are there any other factors that contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts, or is slouching a primary cause?
- What steps can be taken to prevent pilonidal cysts, including improving posture while sitting?

Is there a connection between slouching when sitting and the development of pilonidal cysts?
Pilonidal cysts are a common condition that can cause discomfort and pain in the area around the tailbone. They are usually caused by hair follicles becoming infected and can result in abscesses or sinus tracts. While the exact cause of pilonidal cysts is still not completely understood, there are several factors that are believed to increase the risk of developing the condition. One such factor is poor posture, specifically slouching when sitting.
When we sit with poor posture, such as slouching, we put additional pressure on certain areas of our body, including the tailbone. This increased pressure can lead to irritation and inflammation of the hair follicles in that area, making them more prone to infection. Additionally, slouching can cause the skin to fold and rub against itself, creating a warm and moist environment that is ideal for the growth of bacteria. Over time, these factors can increase the likelihood of developing a pilonidal cyst.
It is important to note that slouching alone is not enough to cause pilonidal cysts. There are other factors involved, such as hair growth patterns, excessive sweating, and genetic predisposition. However, poor posture can contribute to the development and worsening of the condition.
To prevent pilonidal cysts, it is important to maintain good posture when sitting, especially for extended periods of time. This can be achieved by sitting up straight and using a supportive chair or cushion. Taking regular breaks to stretch and move around can also help relieve pressure on the tailbone and prevent the development of cysts.
In addition to maintaining good posture, practicing good hygiene is essential in preventing pilonidal cysts. Keeping the area clean and dry can help reduce the risk of infection. This includes washing the area gently with mild soap and warm water, drying it thoroughly, and avoiding tight clothing that can trap moisture.
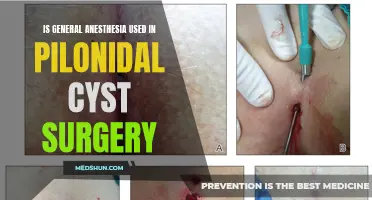
If you already have a pilonidal cyst, it is important to seek medical attention for proper treatment. Depending on the severity of the cyst, treatment options may include antibiotics, draining the abscess, or surgical removal. In some cases, recurrent or severe cysts may require more extensive surgical procedures.
In summary, while slouching when sitting alone does not cause pilonidal cysts, it can contribute to their development and worsening. Maintaining good posture and practicing good hygiene can help prevent the condition. If you already have a pilonidal cyst, it is important to seek medical attention for appropriate treatment.
Heal Cut in Bum Crack with These Effective Methods
You may want to see also

Can poor posture contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts?
Pilonidal cysts are a common skin condition characterized by the formation of small cysts or abscesses in the area between the buttocks. While the exact cause of pilonidal cysts is not fully understood, several factors have been identified as potential contributors to their development. One such factor that has been suggested is poor posture.
Poor posture can refer to a variety of positions and movements that place excessive strain on the body, particularly the lower back and buttocks area. This can include slouching, hunching over a desk, or sitting for extended periods without proper support. These postural habits can lead to increased pressure and friction in the area, which may contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts.
When we sit with poor posture, we place additional stress on the sacrococcygeal area, the region where pilonidal cysts typically occur. The constant pressure and friction caused by poor posture can create an environment that promotes the growth of bacteria, which can then lead to infection and cyst formation. Additionally, poor posture can also disrupt the natural circulation in the area, potentially limiting the body's ability to heal and fight off infections.
To prevent the formation of pilonidal cysts, it is important to maintain good posture throughout the day. This can be achieved by:
- Sitting with proper support: When sitting for prolonged periods, it is essential to use a chair with proper lumbar support. This helps maintain the natural curvature of the spine and reduces the strain on the lower back.
- Taking breaks and stretching: Regular breaks from sitting can help relieve pressure on the buttocks area. During these breaks, it is beneficial to stretch and move around to improve circulation and reduce the risk of cyst formation.
- Using cushions or pillows: For individuals who spend extended periods sitting, such as truck drivers or office workers, using a cushion or pillow can help distribute weight more evenly and reduce pressure on the buttocks.
- Practicing good posture habits: Being mindful of your posture throughout the day can go a long way in preventing pilonidal cysts. This includes sitting up straight, keeping the shoulders back, and engaging the core muscles to support the spine.
It is important to note that while poor posture may contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts, it is not the sole cause. Other factors, such as genetics, trauma to the area, and excessive sweating, can also play a role in their development. Therefore, practicing good posture should be complemented with other preventive measures, such as maintaining proper hygiene and avoiding prolonged sitting or pressure on the buttocks area.
In conclusion, poor posture can potentially contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts by creating an environment that promotes bacterial growth and limits proper circulation. Practicing good posture habits, taking breaks, and using proper support can help reduce the risk of developing these painful cysts. However, it is important to remember that poor posture is just one of several factors that can contribute to their formation, and a comprehensive approach to prevention should be taken.
Can a Cyst Cause a Fever? Exploring the Link Between Cysts and Elevated Body Temperature
You may want to see also

How does slouching lead to the development of pilonidal cysts?
Slouching may seem like a harmless habit, but it can have serious consequences, one of which is the development of pilonidal cysts. Pilonidal cysts are painful, fluid-filled sacs that form in the cleft between the buttocks. They are most commonly found in individuals who sit for long periods of time, such as office workers, truck drivers, and gamers.
So how exactly does slouching lead to the development of pilonidal cysts? Let's break it down step by step:
- Increased pressure: Slouching puts increased pressure on the cleft between the buttocks. This prolonged pressure can cause irritation and inflammation of the skin in that area. When the skin becomes irritated, it can form a small pit or pore, which is a common site for pilonidal cysts to develop.
- Sweating and friction: Slouching often leads to increased sweating and friction in the cleft between the buttocks. This combination of sweat and friction creates a moist, warm environment that is ideal for the growth of bacteria. Bacteria thrive in such conditions and can easily invade the irritated skin, leading to infection and the formation of a cyst.
- Hair follicles: Pilonidal cysts are also commonly associated with ingrown hairs. Slouching can cause the hair in the cleft between the buttocks to become trapped under the skin. Over time, these trapped hairs can lead to the development of a pilonidal cyst.
- Lack of air circulation: Slouching can restrict air circulation in the cleft between the buttocks. This lack of ventilation can further contribute to the growth of bacteria and increase the risk of infection.
To further illustrate this process, let's consider an example. Imagine an office worker who spends long hours sitting at their desk, often in a slouched position. The pressure and friction from their slouching cause irritation in the cleft between their buttocks. This irritation, combined with the lack of air circulation and the presence of trapped hair follicles, creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive. Eventually, an infected pilonidal cyst may develop in the area.
In conclusion, slouching can lead to the development of pilonidal cysts through increased pressure, sweating and friction, trapped hair follicles, and lack of air circulation. It is important to maintain good posture and take regular breaks from sitting to reduce the risk of developing these painful cysts. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as keeping the area clean and dry, can also help prevent the formation of pilonidal cysts.
When Pilonidal Sinus Strikes Again: Can It Come Back?
You may want to see also

Are there any other factors that contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts, or is slouching a primary cause?
Pilonidal cysts are painful sacs filled with pus that typically form in the crease between the buttocks, near the tailbone. While slouching can certainly contribute to the development of these cysts, there are also several other factors that play a role in their formation.
One primary factor that contributes to the formation of pilonidal cysts is the presence of hair. The hair follicles in the area can become irritated and infected, leading to the development of a cyst. This is why pilonidal cysts are often referred to as "hair nest" cysts. The presence of hair, combined with factors like excessive sweating and poor hygiene, can create an environment conducive to cyst formation.
Another factor that contributes to the formation of pilonidal cysts is the shape of the buttocks. People with deep and narrow buttock clefts are more prone to developing these cysts. The tightness of the cleft can cause friction, leading to irritation and infection of the hair follicles.
Additionally, certain lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing pilonidal cysts. People who spend a lot of time sitting or have a sedentary lifestyle are more prone to cyst formation. Sitting for long periods of time puts pressure on the area, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to the development of cysts. This is why pilonidal cysts are often seen in individuals who work desk jobs or spend a significant amount of time driving.
Poor hygiene practices can also contribute to the formation of pilonidal cysts. Failing to keep the buttocks area clean and dry can encourage the growth of bacteria and increase the risk of infection. Excessive sweat and moisture in the area can further exacerbate the problem by providing an ideal breeding ground for bacteria.
It is important to note that slouching can be a contributing factor to the development of pilonidal cysts, but it is not the primary cause. Slouching can increase pressure on the buttocks, compressing the hair follicles and leading to irritation. However, proper posture alone is not enough to prevent the formation of pilonidal cysts. It is crucial to address other factors such as hair removal, hygiene, and overall lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of developing these painful cysts.
To prevent pilonidal cysts, it is recommended to keep the buttocks area clean and dry. Regularly washing the area with mild soap and warm water can help to remove any bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. It is also important to keep the area free from excess hair, as hair removal can help to prevent irritation and subsequent cyst formation. If sitting for long periods of time is unavoidable, taking breaks to stand and stretch can help to alleviate pressure on the buttocks. Additionally, wearing loose-fitting clothing and avoiding excessive sweating can further reduce the risk of pilonidal cysts.
In conclusion, slouching can contribute to the development of pilonidal cysts, but it is not the sole cause. Other factors such as the presence of hair, buttock shape, lifestyle habits, and hygiene practices also play a significant role in cyst formation. It is important to address all of these factors to reduce the risk of developing pilonidal cysts and to maintain good overall health.
The Importance of Recognizing When to Go to the ER for a Pilonidal Cyst
You may want to see also

What steps can be taken to prevent pilonidal cysts, including improving posture while sitting?
Pilonidal cysts are small sacs that form near the tailbone, typically filled with hair and skin debris. They can cause discomfort and pain, making activities such as sitting for prolonged periods quite challenging. However, there are several steps that can be taken to prevent pilonidal cysts, including improving posture while sitting.
- Practice good hygiene: Proper hygiene is key to preventing pilonidal cysts. It is important to keep the area surrounding the tailbone clean and dry. Regular cleansing with mild soap and water can help remove any dirt or bacteria that may lead to cyst formation.
- Maintain a healthy body weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing pilonidal cysts. Excess weight can put pressure on the tailbone area, leading to irritation and inflammation. Maintaining a healthy body weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can help prevent these cysts from forming.
- Avoid sitting for prolonged periods: Extended periods of sitting can increase the pressure on the tailbone area, leading to the development of pilonidal cysts. Taking regular breaks and incorporating short walks or stretches throughout the day can help relieve pressure and reduce the risk of cyst formation.
- Use a cushion or pillow: Sitting on a cushion or pillow can help distribute your weight more evenly and minimize pressure on the tailbone. There are specialized cushions available that are designed to relieve pressure on the coccyx, providing additional support and comfort.
- Maintain proper posture while sitting: Poor posture can place additional stress on the tailbone, increasing the risk of pilonidal cysts. To improve posture while sitting, ensure that your feet are flat on the ground, back is straight, and shoulders are relaxed. Avoid slouching or hunching forward, as this can exacerbate pressure on the tailbone.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight clothing, especially around the tailbone area, can cause friction and irritation, contributing to the formation of pilonidal cysts. Opt for loose-fitting clothing, such as cotton underwear and breathable pants, to reduce the risk of cysts.
- Avoid repetitive friction or trauma: Continuous friction or trauma to the tailbone area can lead to the development of pilonidal cysts. Avoid activities that involve repetitive pressure or trauma to the tailbone, such as cycling or horse riding, as these can increase the risk of cyst formation.
- Seek medical advice if necessary: If you have a history of pilonidal cysts or are experiencing persistent symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can provide guidance and recommend appropriate preventive measures based on your specific situation.
In conclusion, preventing pilonidal cysts involves maintaining good hygiene, practicing proper sitting posture, avoiding prolonged periods of sitting, and taking regular breaks. These simple steps, combined with maintaining a healthy body weight and wearing loose-fitting clothing, can help reduce the risk of cyst formation and ensure overall comfort and well-being.
What to Do When a Pilonidal Cyst Pops: Treatment and Prevention Tips
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, slouching when sitting does not directly cause a pilonidal cyst. A pilonidal cyst is typically caused by a combination of factors such as hair follicles becoming irritated or blocked, excessive sweating, and friction or pressure on the affected area. Slouching may contribute to prolonged pressure and friction in the lower back region, but it is not the sole cause of a pilonidal cyst.
While slouching may not directly cause a pilonidal cyst, there are certain activities and habits that can increase your risk. These include sitting for prolonged periods, especially on hard surfaces or with poor posture, wearing tight clothing that puts pressure on the lower back area, and excessive sweating or poor hygiene in the buttock area. It is important to maintain good posture, take breaks from sitting, and practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of developing a pilonidal cyst.
Sitting on hard surfaces can contribute to the formation of a pilonidal cyst, particularly if done for extended periods with poor posture. Prolonged pressure and friction on the lower back area can irritate hair follicles and lead to the development of a cyst. It is important to use cushioned seats or take frequent breaks from sitting on hard surfaces to reduce the risk of developing a pilonidal cyst.
To prevent a pilonidal cyst from forming, it is important to maintain good posture while sitting and avoid prolonged periods of sitting. Take breaks to stand and stretch or walk around, especially if you have a job or lifestyle that requires long periods of sitting. Practice good hygiene by keeping the buttock area clean and dry, and avoid wearing tight or restrictive clothing that puts pressure on the lower back area.
If you suspect you have a pilonidal cyst, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. They can properly diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options. Treatment may involve simple measures such as warm compresses and pain management, or more advanced interventions such as draining the cyst or surgical removal. It is important to address a pilonidal cyst promptly to prevent complications or recurrence.