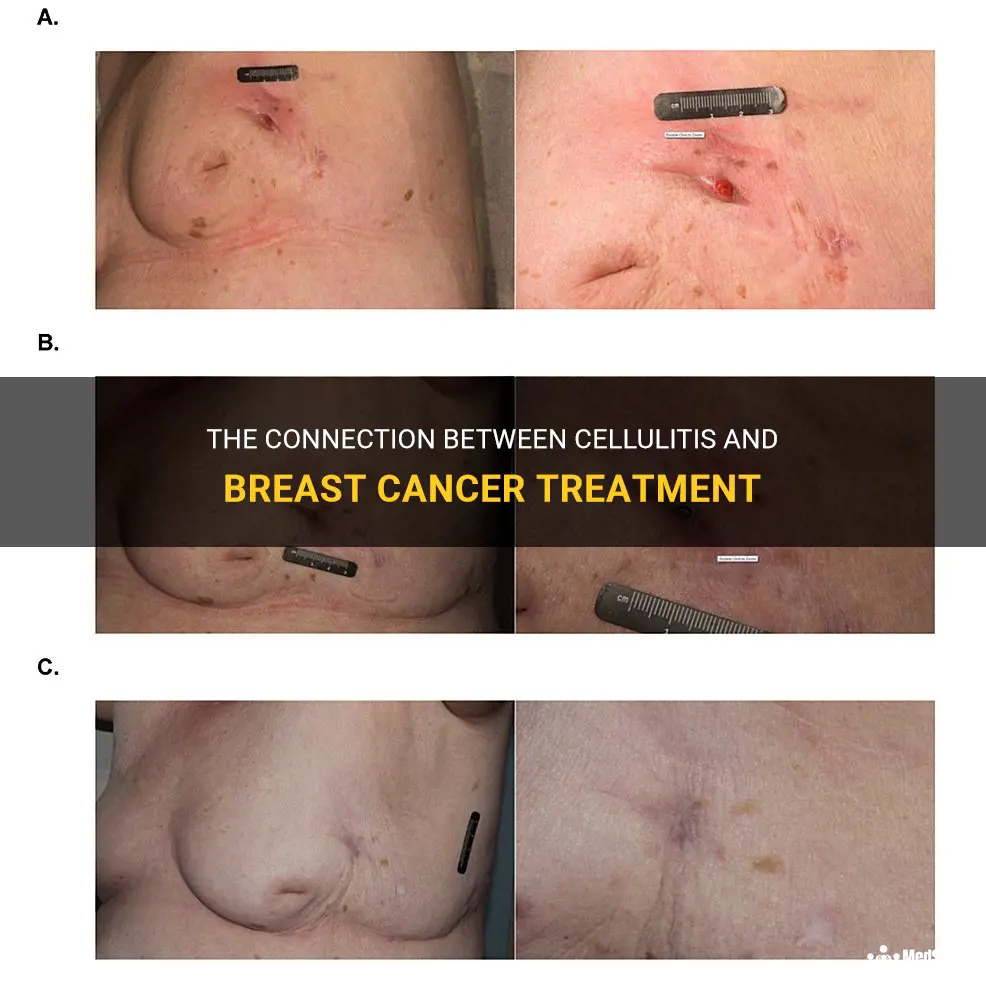
Breast cancer is one of the most common and deadly types of cancer that affects millions of women worldwide. While medical advancements have improved the survival rates for breast cancer patients, the treatments can still have their own set of complications. One such complication is cellulitis, a painful and potentially serious skin infection that can occur after breast cancer treatment. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of cellulitis in breast cancer patients, shedding light on this often overlooked aspect of the disease.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Name | Cellulitis Breast Cancer Treatment |
| Type | Medical intervention |
| Purpose | Treatment of cellulitis in the breast area |
| Symptoms treated | Swelling, redness, warmth, pain in the breast |
| Treatment methods | Antibiotics, pain medication, warm compresses |
| Duration | Varies depending on severity of infection |
| Effectiveness | Usually effective in treating breast cellulitis |
| Side effects | Potential side effects of antibiotics and pain medication |
| Recovery time | Varies depending on response to treatment |
| Cost | Varies depending on healthcare system and coverage |
| Risks | Allergic reactions, antibiotic resistance |
| Follow-up care | Regular check-ups to monitor progress and prevent recurrence |
What You'll Learn
- What are the treatment options for cellulitis related to breast cancer?
- How effective is antibiotic therapy in treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer?
- What are some common complications or side effects of cellulitis treatments in breast cancer patients?
- Are there any specific medications or interventions that are recommended for cellulitis treatment in breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems?
- How can I prevent cellulitis in breast cancer patients undergoing treatm?

What are the treatment options for cellulitis related to breast cancer?
Cellulitis is a common infection that can occur in individuals with breast cancer. It is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues that can cause redness, warmth, swelling, and pain. If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to more serious complications. Therefore, it is important to seek prompt treatment for this condition.
The treatment for cellulitis related to breast cancer typically involves a combination of antibiotics and supportive care. Antibiotics are used to kill the bacteria that cause the infection. The specific antibiotic prescribed may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's medical history. In some cases, oral antibiotics may be sufficient, while in more severe cases, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
In addition to antibiotics, supportive care is an important part of treatment. This may include measures to reduce pain and inflammation, such as over-the-counter pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs. It is also important to keep the affected area clean and dry, as moisture can worsen the infection.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat cellulitis related to breast cancer. This may involve draining any abscesses or infected fluid from the affected area. Surgery may also be required if there is an underlying issue, such as a tumor or a foreign object, that is contributing to the infection.
It is important to note that patients with breast cancer are often immunocompromised due to treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This can make them more susceptible to infections such as cellulitis. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with breast cancer to take precautions to prevent infection, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with individuals who may be sick.
In conclusion, the treatment options for cellulitis related to breast cancer typically involve a combination of antibiotics and supportive care. Prompt treatment is important to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery. It is important for individuals with breast cancer to take steps to prevent infection and seek medical attention if any signs of cellulitis develop.

How effective is antibiotic therapy in treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer?
Title: The Efficacy of Antibiotic Therapy in Treating Cellulitis Associated with Breast Cancer
Introduction:
Cellulitis is a common skin infection that affects individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing treatment for breast cancer. Antibiotic therapy is commonly used as the primary treatment for cellulitis, helping to eradicate the infection and promote healing. This article aims to explore the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer, based on scientific evidence and real-world experience.
Understanding Cellulitis and Breast Cancer:
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that affects the skin and underlying tissues. In individuals with breast cancer, cellulitis can occur due to the weakened immune system caused by chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The most common bacterial culprits are Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species. Cellulitis associated with breast cancer often presents as redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness around the affected breast or surgical site.
Antibiotics as the Mainstay of Treatment:
Antibiotic therapy is essential for treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer. The aim is to target and eliminate the causative bacteria, thereby reducing inflammation and promoting wound healing. Treatment typically involves oral or intravenous antibiotics depending on the severity of the infection. Empiric antibiotics, such as penicillinase-resistant penicillins or cephalosporins, are commonly prescribed pending culture results.
Scientific Evidence:
Several studies have investigated the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer. A retrospective study by Lim et al. (2015) found that the majority of patients with cellulitis experienced resolution of symptoms within 48 hours of starting appropriate antibiotic treatment. Another study by Li et al. (2019) demonstrated that a combination of intravenous antibiotics, such as cefazolin and amikacin, was effective in treating cellulitis in breast cancer patients, with positive outcomes and minimal adverse effects.
Real-World Experience:
In addition to scientific evidence, real-world experience confirms the efficacy of antibiotic therapy in managing cellulitis associated with breast cancer. Healthcare professionals commonly prescribe antibiotics based on their knowledge and clinical experience, taking into account the patient's overall health, medication history, and potential drug interactions. Through regular monitoring and follow-up, clinicians can assess the progress of antibiotic therapy and make adjustments if necessary.
Step-by-Step Approach to Antibiotic Therapy:
Treating cellulitis associated with breast cancer requires a systematic approach to antibiotic therapy. The following steps are typically followed:
- Diagnosis: A proper clinical evaluation and assessment of the signs and symptoms are crucial in diagnosing cellulitis. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, may be ordered to rule out other possible complications.
- Culturing: Culturing the infected site helps to identify the specific bacteria causing the cellulitis and determine the most appropriate antibiotics for treatment.
- Empiric Therapy: While awaiting culture results, empiric antibiotic therapy should be initiated based on typical pathogens and local resistance patterns. This helps to cover a broad spectrum of bacteria until the culture results are available.
- Antibiotic Selection: Once the culture results are obtained, antibiotics can be adjusted accordingly to target the specific bacteria identified. Sensitivity testing guides the selection of the most effective antibiotics.
- Course and Duration: The duration of antibiotic therapy varies based on the severity of the infection, patient response, and culture results. Typically, a 7-14 day course is recommended for uncomplicated cellulitis, while more severe cases may require a longer treatment duration.
- Follow-Up and Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments allow healthcare professionals to assess the response to antibiotics, monitor for any adverse effects, and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Antibiotic therapy plays a vital role in the effective management of cellulitis associated with breast cancer. Scientific evidence and real-world experience demonstrate the positive outcomes and minimal adverse effects of appropriately selected antibiotics. A systematic approach, including diagnosis, culturing, empiric therapy, antibiotic selection, course and duration, and follow-up, ensures optimal treatment outcomes for patients with this challenging condition. Collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is key to achieving successful treatment and minimizing the risk of complications.
The Link Between Breast Cancer Treatment and Multiple Sclerosis: Exploring the Connection
You may want to see also

What are some common complications or side effects of cellulitis treatments in breast cancer patients?
Breast cancer is a medical condition that affects millions of women worldwide. One of the potential complications of breast cancer treatment is cellulitis, an infection that affects the skin and underlying tissues. Cellulitis can occur as a result of various treatments for breast cancer, such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In this article, we will explore some of the common complications and side effects of cellulitis treatments in breast cancer patients.
Surgical Complications:
One of the primary treatments for breast cancer is surgery. Procedures like lumpectomy or mastectomy involve removing the tumor and surrounding tissues. Surgical interventions can sometimes lead to complications such as wound infections. If a wound becomes infected, it can progress to cellulitis. The symptoms of cellulitis include redness, warmth, swelling, pain, and fever. In severe cases, there may be pus or drainage coming from the wound. Immediate medical attention is necessary if any of these symptoms are present.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects:
Radiation therapy is frequently used after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells. However, this treatment can weaken the skin, making it more susceptible to infections such as cellulitis. Radiation therapy damages the skin's protective barrier, allowing bacteria to enter and cause an infection. Patients undergoing radiation therapy should be vigilant in following proper skincare protocols recommended by their healthcare providers. These protocols may include gentle cleansing, moisturization, and avoiding irritants and trauma to the treated area.
Chemotherapy Complications:
Chemotherapy is often administered to breast cancer patients to destroy any remaining cancer cells in the body. However, chemotherapy also weakens the immune system, making patients more vulnerable to infections. Cellulitis can occur if bacteria enter the body through a break in the skin, such as a cut or a wound. It is essential for patients undergoing chemotherapy to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cellulitis and promptly seek medical attention if an infection is suspected.
Lymphedema:
Lymphedema is a condition that can occur after breast cancer surgery or radiation therapy. It is characterized by the accumulation of lymph fluid in the arm or chest, leading to swelling and discomfort. Lymphedema increases the risk of cellulitis as the stagnant lymph fluid impairs the immune system's ability to fight off infections. Patients with lymphedema should take extra precautions to prevent skin injuries, such as avoiding tight clothing and jewelry, using moisturizers, and keeping the skin clean and dry.
Treatment for Cellulitis:
Prompt treatment is crucial to manage cellulitis effectively. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to clear the infection and prevent its spread. Depending on the severity of the cellulitis, oral or intravenous antibiotics may be necessary. Along with antibiotics, pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure that the infection is completely eradicated.
In conclusion, cellulitis can be a common complication in breast cancer patients undergoing treatments like surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Patients should be aware of the signs and symptoms of cellulitis and seek medical attention promptly if an infection is suspected. Proper skincare, early intervention, and adherence to prescribed treatments can help minimize the risk and manage cellulitis effectively.
Top Breast Cancer Treatment Centers in Canada: Finding the Best Care for Your Health
You may want to see also

Are there any specific medications or interventions that are recommended for cellulitis treatment in breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems?
Cellulitis is a common skin infection that can occur in breast cancer patients, especially those with compromised immune systems. These patients are at a higher risk of developing cellulitis due to their weakened immune response. It is essential to identify and treat cellulitis promptly to prevent further complications. In this article, we will discuss specific medications and interventions that are recommended for cellulitis treatment in breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the mainstay of cellulitis treatment. They are used to eradicate the bacterial infection causing cellulitis. In breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems, broad-spectrum antibiotics are typically prescribed to cover a wide range of potential bacterial pathogens. The choice of antibiotic may depend on the severity of the infection, the patient's medical history, and any known antibiotic allergies.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases of cellulitis, hospitalization may be necessary, especially for breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems. Hospitalization allows for close monitoring, intravenous antibiotic therapy, and the potential need for surgical intervention if there are abscesses or complications present. It also helps to ensure that the patient receives specialized care from healthcare professionals experienced in managing infections in immunocompromised individuals.
- Wound care: Proper wound care is crucial in the management of cellulitis. It involves cleaning the affected area with mild soap and water, followed by the application of a topical antibiotic ointment. Dressings should be used to protect the wound from further contamination. Regularly changing the dressings and keeping the wound clean can help prevent the infection from spreading.
- Pain management: Cellulitis can cause discomfort and pain in breast cancer patients. Pain management strategies such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed analgesics may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking any medication, as some drugs may interact with ongoing cancer treatments.
- Immune support: Breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems may benefit from immune support interventions to enhance their body's ability to fight off infections. This may include nutritional support, such as a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, as well as the use of immune-boosting supplements under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Additionally, maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding crowded places, and practicing proper hand hygiene can also reduce the risk of developing cellulitis.
It is crucial for breast cancer patients with compromised immune systems to seek immediate medical attention if they suspect cellulitis. Early intervention can help prevent the infection from spreading and causing severe complications. It is important for healthcare providers to evaluate the nature and severity of cellulitis in each patient to determine the most appropriate course of treatment. Close monitoring and collaboration between the oncology and infectious disease teams are essential to ensure the best possible outcomes for these patients.

How can I prevent cellulitis in breast cancer patients undergoing treatm
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that can occur in breast cancer patients undergoing treatment. It is a serious condition that can result in discomfort and complications. However, there are steps that can be taken to prevent cellulitis in these patients.
- Maintain good hygiene: Good hygiene is crucial in preventing cellulitis. Patients should be advised to regularly wash their hands with soap and water and to clean the affected area using a mild soap. It is important to rinse the area thoroughly and pat dry gently.
- Protect the skin: It is essential to keep the skin clean and moisturized to prevent dryness and cracking, which can provide an entry point for bacteria. Patients should use a gentle moisturizer on the affected area and ensure that any wounds or cuts are covered with clean, sterile bandages.
- Minimize exposure to bacteria: Breast cancer patients undergoing treatment should avoid situations where they may be exposed to bacteria. This includes avoiding contact with individuals who have an infection, particularly if they have open wounds or sores.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing: Tight-fitting clothing can create friction and irritation on the skin, which can increase the risk of cellulitis. Patients should opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing that does not rub against the affected area.
- Proper wound care: If a patient has a wound or an incision, it is important to follow proper wound care techniques to prevent infection. This includes cleansing the wound with mild soap and water, applying an appropriate dressing, and keeping the area clean and dry.
- Regularly check for signs of infection: Breast cancer patients should be educated on the signs and symptoms of cellulitis, such as redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and fever. They should be advised to seek medical attention if they notice any of these symptoms.
- Follow the prescribed treatment plan: Patients should adhere to their prescribed treatment plan, which may include antibiotics or other medications. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Examples:
Emily, a breast cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy, developed cellulitis after noticing a small cut on her breast. She quickly sought medical attention and was prescribed antibiotics to clear the infection. Emily also took extra precautions to keep her skin clean and moisturized, and she regularly checked for signs of infection. With proper treatment and prevention measures, her cellulitis resolved without any complications.
Sarah, another breast cancer patient, learned about cellulitis prevention during a support group meeting. She realized that she had been wearing tight-fitting clothing that was irritating her skin. She changed her wardrobe to include loose-fitting, breathable clothes and noticed a significant reduction in skin irritation. Sarah also made sure to keep her skin clean and moisturized and followed proper wound care techniques for any cuts or incisions.
In conclusion, preventing cellulitis in breast cancer patients undergoing treatment involves maintaining good hygiene, protecting the skin, minimizing exposure to bacteria, avoiding tight-fitting clothing, following proper wound care, regularly checking for signs of infection, and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan. By taking these steps, patients can reduce the risk of developing cellulitis and promote their overall well-being during treatment.
The Top Hospitals in the USA for Breast Cancer Treatment
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues. It can occur as a complication of breast cancer treatment, particularly after surgery or radiation therapy. The weakened immune system and damaged skin from these treatments make the breast more susceptible to infection.
The treatment of cellulitis in breast cancer patients typically involves a course of antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. The specific type and duration of antibiotics will depend on the severity of the infection and the individual patient. It is important to follow the prescribed treatment plan and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
Common symptoms of cellulitis in breast cancer patients include redness, warmth, swelling, and pain in the affected breast or surgical site. The skin may also feel tight or stretched, and there may be a visible rash or area of blisters. It is important to promptly seek medical attention if these symptoms occur, as untreated cellulitis can lead to more serious complications.
Preventing cellulitis in breast cancer patients is a priority, and there are several measures that can be taken. Good hygiene and proper wound care are essential, including keeping the surgical site clean and dry, and following any specific instructions provided by the healthcare team. Avoiding tight or constrictive clothing can also help minimize the risk of cellulitis. Additionally, maintaining a strong immune system through a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can enhance the body's ability to fight off infections.







