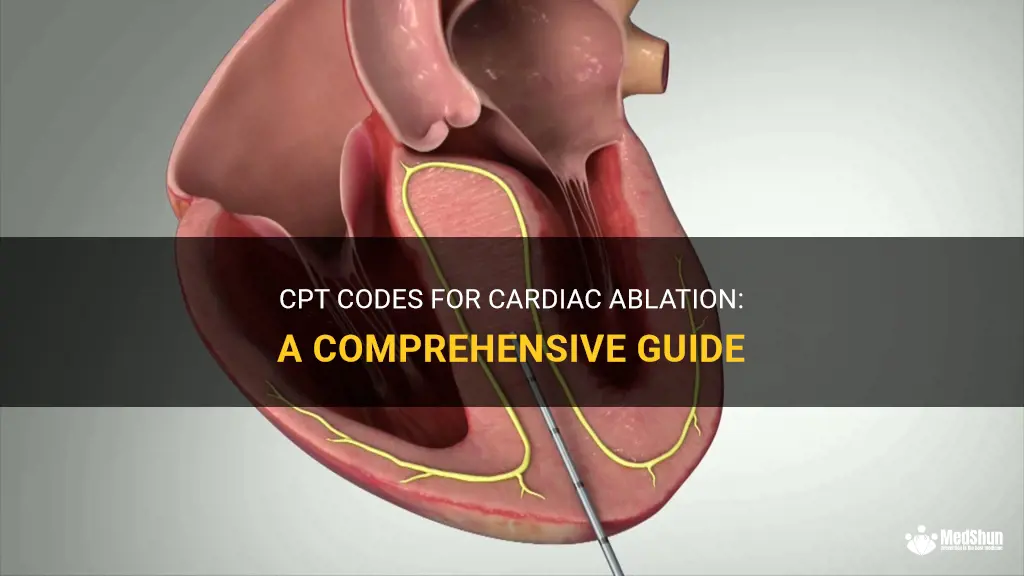
CPT cardiac ablation is a revolutionary medical procedure that offers hope and relief to thousands of individuals suffering from heart rhythm disorders. This advanced technique utilizes radiofrequency energy or extreme cold to precisely target and eliminate the abnormal cardiac tissue causing the irregular heartbeat. While traditional treatments like medications can often help manage the symptoms, cardiac ablation provides a more permanent solution by correcting the underlying issue. This minimally invasive procedure is paving the way for a new era in cardiac care, allowing patients to regain control of their lives and experience a better quality of life.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Cardiac Ablation |
| Purpose | Correct irregular heartbeats |
| Used for | Atrial Fibrillation, Ventricular Tachycardia |
| Catheterization Method | Inserted through blood vessels |
| Energy Sources | Radiofrequency, Laser, Cryothermal, Microwave |
| Duration | Typically 2-4 hours |
| Anesthesia | Local or general |
| Recovery Time | 1-2 days |
| Potential Risks | Infection, Bleeding, Blood Clots, Damage to adjacent structures |
| Success Rate | Varies depending on the condition and patient |
| Prognosis | Generally good with proper follow-up care |
| Follow-up Monitoring | Regular check-ups, EKG, Holter monitor |
| Lifestyle Changes | Regular exercise, Healthy diet, Stress management |
| Medications | May require anti-arrhythmic medications |
| Post-Procedure Care | Limit strenuous activities, Keep incision clean and dry |
| Long-term Effects | Improved quality of life, Reduced symptoms |
What You'll Learn

What is a cardiac ablation procedure?
Cardiac ablation is a medical procedure used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders or arrhythmias. It is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy or cryoablation to destroy or ablate the abnormal tissue that is causing the arrhythmia. The goal of the procedure is to restore normal heart rhythm and alleviate symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fainting.
During a cardiac ablation procedure, the patient is usually placed under general anesthesia or conscious sedation. The cardiologist or electrophysiologist inserts several thin, flexible catheters through small incisions in the groin or arm and guides them to the heart. These catheters generally contain electrodes that can both map and ablate the abnormal tissue.
First, the physician will map the electrical pathways of the heart to identify the areas responsible for the abnormal rhythms. This is done by sending electrical signals through the catheter electrodes and recording the heart's response. The collected data helps the doctor locate the precise area of abnormal tissue that needs to be ablated.
Once the abnormal tissue is identified, the doctor will deliver radiofrequency energy or cold therapy (cryoablation) through the catheter to destroy the tissue. Radiofrequency energy uses heat to create a small burn or scar on the abnormal tissue, while cryoablation freezes and destroys the abnormal tissue. Both methods are effective in interrupting the abnormal electrical signals that cause the arrhythmia.
The procedure is typically monitored through imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy, which allows the doctor to visualize the catheters and their position within the heart. In some cases, a three-dimensional mapping system is also used to aid in the visualization and accuracy of the ablation procedure.
After the ablation is complete, the cardiologist will test to ensure the abnormal rhythms have been eliminated. This may involve inducing the arrhythmia using medications or electrical stimulation to confirm the success of the procedure. If the arrhythmia is no longer present, it indicates a successful ablation.
Following the procedure, patients are required to stay in the hospital for monitoring and observation for a brief period. They may experience some discomfort at the catheter insertion sites, but this generally resolves within a few days. Most patients can resume normal activities within a week or two, although strenuous physical activity may be limited for a certain period.
Cardiac ablation procedures have a high success rate in treating various arrhythmias, and the risk of complications is relatively low. However, like any medical procedure, there are potential risks involved, such as bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or nerves, or even heart perforation. The cardiologist will discuss these risks with the patient and ensure they understand the benefits and potential drawbacks before proceeding with the procedure.
In conclusion, cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat heart rhythm disorders or arrhythmias. It involves mapping the electrical pathways of the heart and using radiofrequency energy or cryoablation to destroy the abnormal tissue causing the arrhythmia. The procedure has a high success rate and can provide significant relief from arrhythmia symptoms, allowing patients to resume a normal and healthy lifestyle.
The Benefits and Considerations of Radiofrequency Ablation for Treating Tongue Conditions
You may want to see also

How is cardiac ablation performed?
Cardiac ablation is a procedure used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders, such as atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into the heart to destroy or block abnormal electrical pathways that are causing the rhythm disorder.
The procedure is typically performed in a specialized cardiac catheterization lab by a team of electrophysiologists, nurses, and technicians. It involves several steps to ensure a successful outcome:
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is given medication to help them relax and reduce any discomfort. The area where the catheter will be inserted, often the groin or the arm, is cleaned and sterilized.
- Numbing the area: A local anesthetic is injected into the skin and tissues near the entry site to numb the area and prevent pain during catheter insertion.
- Inserting the catheter: A small incision is made at the entry site, and a catheter (a long, thin tube) is threaded through a blood vessel and guided into the heart. The catheter is equipped with electrodes at its tip, which are used to pinpoint the abnormal electrical pathways.
- Mapping the heart: Once the catheter is in place, a process called cardiac mapping is performed. The electrodes on the catheter record the electrical signals in different areas of the heart, helping the electrophysiologist identify the exact location of the abnormal pathway.
- Ablating the tissue: After mapping the heart, the electrophysiologist uses radiofrequency energy or cryotherapy (extreme cold) to destroy or scar the tissue responsible for the abnormal electrical signals. This process is known as ablation. The specific method used depends on the type and location of the abnormal pathway.
- Evaluating the results: After each ablation, the electrophysiologist tests the heart's electrical signals to ensure that the abnormal pathway has been successfully blocked or destroyed. This may involve pacing the heart or inducing the arrhythmia to determine its response.
- Repeat ablations: In some cases, multiple ablations may be necessary to completely eliminate the abnormal pathways. This is especially true for complex or persistent rhythm disorders.
Throughout the procedure, the patient's vital signs, such as blood pressure and heart rate, are continuously monitored to ensure their safety and comfort. After the ablation is complete, the catheter is carefully removed, and the entry site is closed with sutures or special closure devices.
While cardiac ablation is generally safe and effective, there are some risks associated with the procedure, including bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or heart valves, and the formation of blood clots. However, serious complications are rare.
In conclusion, cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that can successfully treat certain heart rhythm disorders. It involves the use of catheters and specialized techniques to block or destroy abnormal electrical pathways in the heart. As with any medical procedure, it is important to discuss the benefits, risks, and potential alternatives with a healthcare provider before considering cardiac ablation.
Understanding the Differences: Unipolar vs Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation
You may want to see also

What conditions can be treated with cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is a medical procedure used to treat a variety of heart conditions. It involves using radiofrequency or cryoenergy to create small scars or lesions on the heart tissue, which can help to correct irregular heart rhythms. Here are some of the conditions that can be treated with cardiac ablation:
- Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder that causes the upper chambers of the heart to beat irregularly. This can lead to a rapid and irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Cardiac ablation can be used to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that are causing the irregular rhythm.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Ventricular tachycardia is a potentially life-threatening condition that causes the lower chambers of the heart to beat too quickly. It can lead to dizziness, chest pain, and in severe cases, cardiac arrest. Cardiac ablation can be used to remove the abnormal tissue causing the rapid heartbeats and restore a normal rhythm.
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT): AVNRT is a common type of cardiac arrhythmia that occurs when there is an abnormal electrical pathway in the heart. This can cause rapid and regular heartbeats, which can lead to symptoms such as palpitations and lightheadedness. Cardiac ablation can be used to eliminate the abnormal pathway and restore a regular heart rhythm.
- Accessory Pathways: Some people are born with abnormal electrical connections in their hearts called accessory pathways. These pathways can cause a rapid heartbeat known as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Cardiac ablation can be used to destroy these pathways and prevent episodes of rapid heartbeats.
- Atrial Flutter: Atrial flutter is a condition characterized by a rapid and regular heartbeat in the upper chambers of the heart. It can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Cardiac ablation can be used to destroy the abnormal electrical circuits in the heart responsible for the flutter and restore a normal rhythm.
During a cardiac ablation procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin or arm and guided to the heart. Energy, such as radiofrequency or cryoenergy, is then used to create small scars or lesions on the heart tissue. These scars block the abnormal electrical signals and restore a normal rhythm.
While cardiac ablation is generally safe, it does carry some risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to the heart or blood vessels. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your doctor before undergoing this procedure.
In conclusion, cardiac ablation is an effective treatment option for several heart conditions, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, AVNRT, accessory pathways, and atrial flutter. It can help to restore a normal heart rhythm and improve symptoms in patients with these conditions. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if cardiac ablation is the right treatment option for you.

What are the potential risks and complications associated with cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is a procedure used to treat certain heart rhythm disorders, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and supraventricular tachycardia. While it is generally considered a safe and effective treatment option, there are potential risks and complications associated with the procedure.
One potential risk is bleeding. During the ablation procedure, small incisions are made in the groin area to access the blood vessels and navigate to the heart. These incisions can sometimes lead to bleeding. The risk of bleeding can be minimized by applying pressure to the incision site after the procedure and closely monitoring the patient's vital signs.
Another potential risk is infection. Any time the skin is pierced, there is a risk of infection. This risk can be mitigated by properly sterilizing the equipment used during the procedure and following strict infection control protocols. In addition, patients are typically prescribed antibiotics before and after the procedure to further reduce the risk of infection.
One of the most serious complications of cardiac ablation is damage to the blood vessels or the heart itself. The catheter used during the procedure can cause injury to the blood vessels or heart tissue if not carefully maneuvered. This can lead to bleeding, heart attack, or stroke. To minimize this risk, experienced and skilled electrophysiologists perform the procedure and use imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy or intracardiac echocardiography, to guide the catheter and ensure its proper placement.
Another potential complication is the formation of blood clots. Cardiac ablation can disrupt the normal flow of blood in the heart, which can increase the risk of blood clot formation. If a blood clot forms, it can potentially travel to other parts of the body and cause a stroke or other serious complications. To prevent blood clots, patients are often prescribed anticoagulant medications before and after the procedure.
There is also a risk of damage to the heart's electrical system during the ablation procedure. The goal of cardiac ablation is to destroy or disrupt the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that are causing the rhythm disorder. However, there is a small risk of inadvertently damaging the normal electrical pathways, which can lead to a new heart rhythm problem. This risk is minimized by careful mapping of the heart's electrical system before the ablation and using techniques to precisely target the abnormal pathways.
In rare cases, cardiac ablation can lead to a weakened heart muscle or heart failure. This can occur if the ablation procedure inadvertently damages healthy heart tissue or if the heart develops scar tissue as a result of the procedure. These complications are rare and can often be managed with medication or other interventions if they occur.
It is important for patients considering cardiac ablation to discuss the potential risks and complications with their healthcare provider. While the procedure can offer significant benefits in terms of improving heart rhythm and quality of life, it is important to understand and weigh the potential risks before making a decision. With careful planning, skilled operators, and appropriate follow-up care, the risks and complications of cardiac ablation can be minimized.
Understanding the Downtime Associated with Radiofrequency Endovenous Ablation
You may want to see also

What is the success rate of cardiac ablation in treating and managing heart conditions?
Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart, where it delivers energy (such as heat or cold) to destroy or disrupt the abnormal heart tissue causing the arrhythmia.
The success rate of cardiac ablation varies depending on several factors, including the type and location of the arrhythmia, the skill and experience of the healthcare provider performing the procedure, and the overall health of the patient. However, studies have shown that cardiac ablation is generally highly successful in treating and managing heart conditions.
In a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, researchers found that cardiac ablation had a success rate of approximately 80% in treating atrial fibrillation, the most common type of arrhythmia. Another study published in the same journal reported a success rate of 90% for supraventricular tachycardia, another common arrhythmia.
One of the benefits of cardiac ablation is its ability to provide long-term relief from arrhythmias. Unlike medications, which may only provide temporary relief, cardiac ablation can effectively eliminate the abnormal heart tissue, preventing the arrhythmia from returning in many cases. This can greatly improve the quality of life for patients with chronic arrhythmias.
For example, John, a 45-year-old man, had been living with atrial fibrillation for several years. His symptoms included palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Medications had only provided partial relief, and he was growing increasingly frustrated and limited in his daily activities. After discussing his options with his cardiologist, John decided to undergo cardiac ablation.
During the procedure, John's cardiologist identified the areas of his heart that were causing the abnormal heart rhythm and carefully destroyed the tissue using radiofrequency energy. Following the procedure, John experienced a significant improvement in his symptoms. His heart rhythm returned to normal, and he was able to resume his regular activities without limitations.
While cardiac ablation is generally safe and effective, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks. There is a small risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, or damage to the heart or blood vessels. However, these risks are relatively low, and serious complications are rare.
In summary, cardiac ablation is a highly successful procedure for treating and managing heart conditions, particularly arrhythmias. It offers long-term relief and can greatly improve the quality of life for patients. However, it is important for individuals considering cardiac ablation to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider to determine if it is the right treatment option for them.
Understanding Endometrial Ablation Sunechiae: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat various heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias). During the procedure, a catheter is threaded through a blood vessel to the heart, where it delivers energy to specific areas that are causing the arrhythmia. This energy can be used to destroy or modify the abnormal heart tissue that is causing the problem.
The length of a cardiac ablation procedure can vary depending on several factors, such as the type of arrhythmia being treated and the complexity of the case. On average, the procedure typically takes about 2 to 4 hours to complete.
Cardiac ablation can be a highly effective treatment option for many types of arrhythmias, and it can often provide long-term relief. However, it is important to note that some arrhythmias may require multiple ablation procedures or additional treatments over time. The success and durability of cardiac ablation can also vary from person to person.
Like any medical procedure, cardiac ablation carries some potential risks and complications. These can include bleeding or bruising at the catheter insertion site, infection, damage to the blood vessels or heart valves, the formation of blood clots, and damage to the heart or surrounding structures. It is important to discuss these potential risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
The recovery process after cardiac ablation can vary from person to person, but most individuals can expect to spend at least one night in the hospital for monitoring. After the procedure, there may be some discomfort or soreness at the catheter insertion site, and some patients may experience temporary fatigue or palpitations. It is important to follow your healthcare provider's post-procedure instructions regarding activity restrictions, medications, and follow-up appointments. Most individuals can resume their normal activities within a few days to a week after the procedure.






5 Comments
Willie Nixon
Madalyn Delgado
Yury Trafimovich
AuthorLorelai Mcneil
Alex Alikiotis
Author