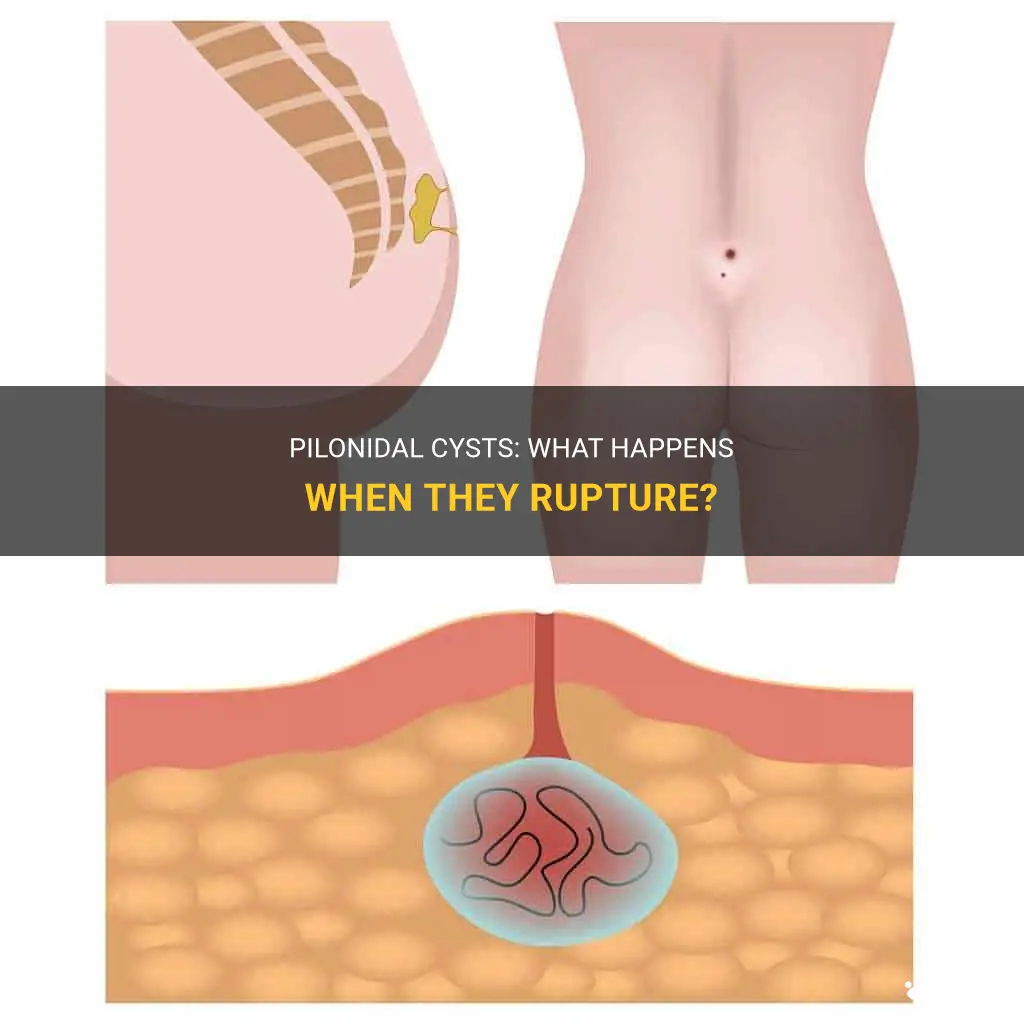
Pilonidal cysts, also known as pilonidal sinus, can be an extremely painful and bothersome condition. These cysts are typically found near the tailbone area and can become inflamed or infected, causing discomfort and potentially leading to the formation of an abscess. In some cases, these cysts may rupture, which can be both a relief and a cause for concern. This intriguing phenomenon of pilonidal cyst rupture is a topic that merits closer examination, as it explores the potential implications, complications, and steps for management to ensure optimal outcomes for those affected by this condition.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Location of cyst | Sacrococcygeal region |
| Appearance | Red, swollen, painful |
| Fluid leakage | Pus or blood |
| Foul odor | Yes |
| Fever | Possible fever |
| Recurrence | Common |
| Risk factors | Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history |
What You'll Learn
- What are the common symptoms of a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
- How is a ruptured pilonidal cyst typically diagnosed by a healthcare professional?
- What are the potential complications of a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
- What are the recommended treatment options for a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
- How can someone prevent a pilonidal cyst from becoming infected or rupturing?

What are the common symptoms of a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
A pilonidal cyst is a painful skin condition that usually forms near the tailbone (coccyx) or between the buttocks. It occurs when hair follicles become blocked and infected, leading to the formation of a pocket of pus. In some cases, the cyst may rupture, causing a range of symptoms and complications. There are several common symptoms of a ruptured pilonidal cyst that individuals should be aware of in order to seek medical attention promptly.
One of the most noticeable symptoms of a ruptured pilonidal cyst is severe pain in the affected area. The pain may be throbbing or sharp and may radiate to the surrounding skin. The pain can make it difficult to sit, walk, or perform everyday activities.
Another symptom of a ruptured pilonidal cyst is the presence of pus or blood drainage from the cyst. The cyst may develop a small opening, allowing the discharge to escape. This drainage may have a foul odor and can stain clothing or bedding.
In addition to pain and drainage, a ruptured pilonidal cyst may cause redness and swelling in the surrounding skin. The area may feel warm to the touch and may be tender or sore. The skin may also appear overlying the cyst may appear stretched or shiny.
If the infection from a ruptured pilonidal cyst spreads, individuals may experience symptoms such as fever, chills, and a general feeling of unwellness. These systemic symptoms indicate a more severe infection and should prompt immediate medical attention.
It is important to note that not all pilonidal cysts rupture, and some individuals may only experience mild symptoms. However, if a cyst does rupture, it is important to seek medical attention. Untreated or poorly managed cysts can lead to chronic infections, abscesses, and the formation of sinus tracts, which are narrow channels that extend from the cyst.
If a ruptured pilonidal cyst is suspected, a healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess the area and determine the appropriate course of treatment. They may order additional tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, to evaluate the extent of the infection.
Treatment for a ruptured pilonidal cyst typically involves a combination of home care and medical interventions. Home care may include keeping the area clean and dry, applying warm compresses to the area, and avoiding prolonged sitting. Medications such as antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend draining the cyst or performing a procedure to remove the cyst entirely. This may involve draining the cyst and packing it with gauze to promote healing, or in more severe cases, surgically excising the cyst and surrounding tissue.
Preventing the formation of pilonidal cysts and the risk of rupture can be challenging, as the exact cause is unknown. However, there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk. These include practicing good hygiene by keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding prolonged sitting or pressure on the area, and wearing loose-fitting clothing. Additionally, individuals who are prone to recurrent cysts may benefit from hair removal methods such as shaving or waxing.
In conclusion, a ruptured pilonidal cyst can cause a range of symptoms, including severe pain, drainage, redness, and swelling. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent complications and manage the infection effectively. By practicing good hygiene and taking preventative measures, individuals can reduce the risk of developing pilonidal cysts and the potential for rupture.
The Importance of Recognizing When to Go to the ER for a Pilonidal Cyst
You may want to see also

How is a ruptured pilonidal cyst typically diagnosed by a healthcare professional?
A ruptured pilonidal cyst is a painful and often uncomfortable condition that requires medical attention. This type of cyst typically occurs near the tailbone and is filled with pus and fluid. When it ruptures, it can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, swelling, redness, and bleeding.
Diagnosing a ruptured pilonidal cyst typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. Here is a step-by-step guide on how healthcare professionals typically diagnose this condition:
- Medical history review: The first step in diagnosing a ruptured pilonidal cyst is to review the patient's medical history. The healthcare professional will ask about the patient's symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and discharge. They will also inquire about any previous history of pilonidal cysts or other relevant medical conditions.
- Physical examination: After reviewing the medical history, the healthcare professional will perform a physical examination. They will inspect the affected area and look for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, and discharge. They may also gently palpate the area to assess tenderness and the presence of a fluctuant mass.
- Visual inspection: In some cases, the healthcare professional may use a tool called a speculum to visualize the inside of the pilonidal cyst. This can help assess the extent of the rupture and any underlying sinus tracts.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, the healthcare professional may order imaging tests to further evaluate the condition. This can include ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. These imaging tests can provide detailed information about the extent of the infection, the presence of abscesses, and any sinus tracts or tunnels.
- Laboratory tests: To confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the infection, the healthcare professional may order laboratory tests. This can include a complete blood count (CBC) to assess for signs of infection, such as an elevated white blood cell count. They may also collect a sample of the cyst fluid for culture and sensitivity testing to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
Once a healthcare professional has diagnosed a ruptured pilonidal cyst, the treatment plan can be determined. This typically involves a combination of conservative management, such as warm compresses, pain medications, and antibiotics, as well as more invasive interventions if necessary, such as incision and drainage or surgical removal of the cyst and affected tissue.
In conclusion, diagnosing a ruptured pilonidal cyst involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and potentially imaging and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional will assess the symptoms, inspect the affected area, and use tools such as a speculum to visualize the cyst and any underlying sinus tracts. Imaging tests and laboratory tests can provide further information to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Effective Ways to Treat Cystic Ingrown Hair
You may want to see also

What are the potential complications of a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
A pilonidal cyst is a small, fluid-filled sac that develops near the tailbone or coccyx. It typically contains hair and skin debris, and can become infected and cause pain. In some cases, a pilonidal cyst may rupture, leading to a variety of potential complications.
One potential complication of a ruptured pilonidal cyst is an abscess. When the cyst ruptures, bacteria from the surrounding skin can enter the cyst and cause an infection. This can result in the formation of an abscess, which is a pocket of pus that forms in the body. Abscesses can be extremely painful and may require medical intervention, such as drainage or antibiotics, to treat the infection.
Another potential complication of a ruptured pilonidal cyst is the formation of a sinus tract. A sinus tract is a narrow, tunnel-like passage that forms between the infected cyst and the surface of the skin. This passage allows for the drainage of pus and other fluids from the cyst, but it can also become infected and cause further complications. The sinus tract can fill with bacteria and debris, resulting in recurrent infections and the formation of additional abscesses.
In some cases, a ruptured pilonidal cyst can lead to the development of a chronic pilonidal sinus. A chronic pilonidal sinus is a long-lasting, recurrent condition that is characterized by the presence of one or more sinus tracts in the affected area. These sinus tracts may drain intermittently and can be associated with ongoing pain, swelling, and discomfort. Chronic pilonidal sinuses often require surgical intervention to fully resolve the condition.
If a ruptured pilonidal cyst is not properly treated, it can also lead to the development of a pilonidal fistula. A pilonidal fistula is a connection between the infected cyst and another nearby structure, such as the anus or rectum. This can lead to the spread of infection to other parts of the body, as well as the development of further complications, such as an anal abscess. Pilonidal fistulas typically require surgical intervention to remove the fistula and promote healing.
In summary, a ruptured pilonidal cyst can result in a variety of potential complications, including abscess formation, the development of a sinus tract, the formation of a chronic pilonidal sinus, and the development of a pilonidal fistula. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a pilonidal cyst or if you experience any symptoms of infection or complications, as prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and promote healing.
EXAMPLE:
John had been suffering from pain in his tailbone for several weeks. He felt a small lump in the area and assumed it was a pilonidal cyst. One day, while he was sitting at his desk, he felt a sudden intense pain in his tailbone, and noticed that the lump had burst. Not knowing what to do, he decided to wait and see if it would heal on its own.
Over the next few days, John noticed that the pain and swelling in the area had worsened. He also developed a high fever and noticed that pus was draining from the site where the cyst had burst. Concerned about his symptoms, he made an appointment with his doctor.
After a thorough examination, the doctor confirmed that John had a ruptured pilonidal cyst and that it had become infected, leading to the formation of an abscess. The doctor explained that the infection needed to be treated promptly to avoid further complications.
John was prescribed a course of antibiotics and was also scheduled for a procedure to drain the abscess. The procedure was performed under local anesthesia, and John experienced immediate relief from the pain and discomfort.
During the procedure, the doctor also noted the presence of a sinus tract leading away from the abscess. The doctor explained that if the sinus tract was not fully treated, it could lead to recurrent infections and the formation of additional abscesses.
As part of his treatment plan, John was scheduled for a follow-up procedure to remove the sinus tract and prevent future complications. The second procedure was successful, and John experienced complete resolution of his symptoms.
Through this experience, John learned the importance of seeking timely medical attention for a ruptured pilonidal cyst. He now understands the potential complications that can arise from an untreated cyst, and he is committed to maintaining good hygiene and taking any necessary preventive measures to avoid a recurrence.
Understanding the Causes and Treatment of Abscesses on the Buttocks
You may want to see also

What are the recommended treatment options for a ruptured pilonidal cyst?
A ruptured pilonidal cyst can cause significant pain and discomfort. It occurs when a cyst in the area between the buttocks becomes infected and bursts, leading to the release of pus and blood. If you have experienced a ruptured pilonidal cyst, there are several treatment options available that can help alleviate your symptoms and promote healing.
Cleaning and Dressing the Wound:
One of the first steps in treating a ruptured pilonidal cyst is to clean the wound thoroughly. This can be done by gently washing the area with warm water and mild soap. It is important to avoid any harsh soaps or scrubbing that may irritate the skin further. Once the area is clean, a sterile dressing should be applied to keep the wound protected and to promote healing.
Antibiotics:
The infection associated with a ruptured pilonidal cyst often requires the use of antibiotics to help fight the bacteria causing the infection. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate antibiotic based on the severity of the infection and any underlying conditions you may have.
Pain Management:
Ruptured pilonidal cysts can be quite painful, and managing the pain is an essential part of the treatment process. Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to help alleviate the pain. In more severe cases, stronger pain medications may be prescribed.
Warm Compresses:
Applying warm compresses to the area can provide relief from pain and help reduce inflammation. The heat increases blood flow to the area, promoting healing by bringing important nutrients and oxygen to the wounded tissues.
Rest and Limited Physical Activity:
It is important to give your body time to heal by resting and avoiding activities that put excessive pressure on the affected area. This may include avoiding sitting for long periods, avoiding activities that involve repetitive movements of the lower back and buttocks, and avoiding any activities that may cause excessive sweating or friction in the area.
Surgical Options:
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat a ruptured pilonidal cyst. Surgical options may include drainage and debridement, where the cyst is opened and cleaned, or complete excision of the cyst and surrounding tissue. The choice of surgical procedure will depend on the severity and chronicity of the cyst.
It is important to note that these treatment options are recommended for a ruptured pilonidal cyst. However, prevention is always better than treatment. To prevent the recurrence of pilonidal cysts, it is important to maintain good hygiene, keep the area clean and dry, avoid prolonged sitting, and wear loose-fitting clothes to reduce friction in the area.
In conclusion, a ruptured pilonidal cyst can be a painful and uncomfortable condition. However, with proper treatment and care, healing can be achieved. Cleaning and dressing the wound, taking antibiotics, managing pain, applying warm compresses, resting, and limited physical activity are all recommended treatment options. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Remember, prevention is key, so maintaining good hygiene and taking preventive measures can help avoid pilonidal cysts in the future. If you are experiencing symptoms of a ruptured pilonidal cyst, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Should I Shave Around a Burst Pilonidal Cyst? How to Approach Hair Removal Safely
You may want to see also

How can someone prevent a pilonidal cyst from becoming infected or rupturing?
Pilonidal cysts are a common condition that can be quite painful and uncomfortable. They occur near the tailbone and can become infected or rupture, which can cause even more complications. However, there are steps that can be taken to prevent these cysts from becoming infected or rupturing.
First and foremost, maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing infection and rupture of pilonidal cysts. Keeping the area clean and dry is essential to prevent the growth of bacteria. Washing the area with mild soap and warm water regularly can help to reduce the risk of infection. It is also recommended to use a clean, dry towel to pat the area dry gently after washing.
Another important precaution to take is to avoid prolonged sitting or sitting in positions that put pressure on the cyst. Sitting for long periods of time can increase the risk of cyst rupture. It is advised to take regular breaks from sitting and to avoid sitting on hard surfaces. Using a cushion or pillow to support the tailbone while sitting may also help to reduce the risk of cyst rupture.
Wearing loose-fitting clothing is also important in preventing the cyst from becoming infected or rupturing. Tight clothing can cause friction and irritation, which can lead to the breakdown of the skin overlying the cyst. Opting for loose, breathable clothing can help to minimize irritation and reduce the risk of infection or rupture.
In some cases, a pilonidal cyst may need to be drained or surgically removed to prevent infection or rupture. This decision is usually made by a healthcare professional who will evaluate the size, location, and severity of the cyst. If drainage or surgery is necessary, it is important to follow the post-procedure instructions provided by the healthcare professional. This may include keeping the area clean and dry, applying antibiotic ointment, and avoiding activities that can put strain on the area.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can aid in preventing pilonidal cysts from becoming infected or rupturing. Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress levels can all contribute to overall health and wellbeing. These factors can help to strengthen the immune system, reducing the risk of infection. Proper nutrition can also promote the healing of any existing cysts and prevent the development of new ones.
In conclusion, preventing pilonidal cysts from becoming infected or rupturing is possible through proper hygiene, avoiding prolonged sitting, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Following these steps can help to alleviate discomfort and reduce the risk of complications associated with pilonidal cysts. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan if you suspect you have a pilonidal cyst.
Understanding How a Pilonidal Cyst Can Lead to Back Pain
You may want to see also